What is Cosmetic Acne?
The development of different types of acne lesions like whiteheads, blackheads, small papules and inflamed pustules as a result of the application of cosmetics on different areas like cheeks, chin and forehead is termed as Cosmetic Acne.
How Does Cosmetic Causes Acne?
There are many factors responsible for the cause of acne. The use and the effect of cosmetics, makeup and other beauty products that are applied to the face, neck, hair and other parts of the body is one such factor responsible for the cause of acne. This is because these cosmetics contain vegetable oil and other chemical ingredients like lanolin, stearic acid, oleic acid, lauryl alcohol etc that can clog the pores, induce follicular irritation and produce more comedones. This ability of cosmetics to induce comedones is known as Comedogenicity. Certain greasy cosmetics may alter the follicular cells and make them stick together.
Several hair care products like shampoo, conditioner, hair oil etc do not easily get washed off. If any of these products trickle down to the face then they could block the pores which ultimately lead to acne breakouts.
Many body care products like soaps, body wash, exfoliating scrubs, lotions, greasy skin creams, body gels etc may not easily get washed off and so they remain on the skin’s surface which ultimately clog the pores and cause skin irritation.
How to Identify Acne Cosmetica?
Acne Cosmetica or the acne caused by cosmetics is a mild form of acne. This type of acne is identified by small, tiny and pink whiteheads clustering over the cheek, chin and forehead. It develops over a period of a few weeks or months and may persist for a long time. It does not result in scarring but it is uncomfortable like all other forms of acne.
Acne Causing Cosmetics:
Certain beauty products which cause cosmetic acne includes makeup, foundation, moisturizer, talcum powder, pomades, face pack, face wash, sunscreen lotions, tanning lotions, hair care products like shampoo, conditioner, hair gel, hair oil, body care products like soaps, body wash, exfoliating scrubs, heavy greasy skin creams, body gels etc.
Cosmetic Acne Skin Care Regimen:
Cosmetic acne skin care regimen is an essential and effective technique incorporated for cleaning the underneath skin before the application of cosmetics in order to prevent the occurrence of acne cosmetica. The different steps of a skin care regimen before and after the application of cosmetics are as follows:
Acne Skin Care Regimen before Applying Cosmetics:
Step 1: Before applying cosmetics, Wash your face with suitable face wash to remove oil and dirt. While washing do not scrub but just apply gentle massage to avoid scratching.
Step 2: Rinse your face with cold or lukewarm water as hot water may irritate your skin and open the pores.
Step 3: Apply appropriate cleanser and tonner by using wipes to clean the pores.
Step 4: Now apply the moisturizer with SPF to protect your skin from sun and to clear the skin from excessive oil.
Step 5: Use the oil free or non-comedogenic cosmetics with natural ingredients to prevent clogging your pores and leave the skin healthier.
Acne Skin Care Regimen after Applying Cosmetics:
Step 1: For those who regularly use makeup in their daily routine, it is very essential to remove makeup at nights before going to bed in order to prevent clogging and maintain a healthy and acne free skin.
Step 2: To remove makeup, cleanse your face with suitable face wash to remove all the traces of makeup.
Step 3: Do not scrub while washing to avoid scratching and skin irritation. Avoid over washing as it may lead to skin dryness.
Step 4: Rinse your face with cold or lukewarm water.
Step 5: Keep your hair and body clean to prevent acne breakouts.
Cosmetic Acne Treatment:
It is easier to treat cosmetic acne as compared to hormonal and hereditary acne. Important remedies for the treatment and prevention of cosmetic acne are as follows:
1) Always make a note of your skin’s reaction whenever you use any new cosmetic product. If you find the development of acne due to the use of this new cosmetic product then stop using that particular product and make a note of the changes on the skin.
2) Always use oil free cosmetics with natural ingredients to prevent acne breakouts. Always purchase non-comedogenic products while shopping for makeup or any other skin and hair care products.
3) Always follow the cosmetic acne skin care regimen before and after the application of cosmetics to maintain healthy skin.
4) Maintain a healthy and well-balanced diet with lots of fresh fruits and vegetables. Avoid eating junk and oily food.
5) Perform yoga and exercise on a regular basis.
Friday, April 10, 2009
Acne Vitamins:
 Several Acne Vitamins like vitamin A, B-Complex, C, D, E, K and minerals like zinc, chromium and selenium play an important role in maintaining healthy skin tissues. They also contribute in acne prevention and heeling acne faster. This is because these vitamins are powerful antioxidants that clear the pores by flushing toxins and free radicals outside the body. Some even have antibacterial properties which help in healing the damaged skin tissues by promoting immunity. Deficiency of these vitamins and minerals can cause acne. Thus, it is recommended to have 3-5 servings of different fruits and vegetables to obtain all essential vitamins and minerals for a healthy and acne free skin. Some facts about essential Acne Vitamins and Minerals are listed below.
Several Acne Vitamins like vitamin A, B-Complex, C, D, E, K and minerals like zinc, chromium and selenium play an important role in maintaining healthy skin tissues. They also contribute in acne prevention and heeling acne faster. This is because these vitamins are powerful antioxidants that clear the pores by flushing toxins and free radicals outside the body. Some even have antibacterial properties which help in healing the damaged skin tissues by promoting immunity. Deficiency of these vitamins and minerals can cause acne. Thus, it is recommended to have 3-5 servings of different fruits and vegetables to obtain all essential vitamins and minerals for a healthy and acne free skin. Some facts about essential Acne Vitamins and Minerals are listed below.1) Vitamin A:

 Vitamin A is a fat soluble vitamin that exists in different forms. Vitamin A obtained from animal sources is called Retinol while its provitamin obtained from plant sources is called Beta-Carotene.
Vitamin A is a fat soluble vitamin that exists in different forms. Vitamin A obtained from animal sources is called Retinol while its provitamin obtained from plant sources is called Beta-Carotene.Dermatological Functions:
Vitamin A is important in maintaining healthy skin. It strengthens the protective tissue of the skin and mucus membrane. It prevents the formation of acne by reducing sebum production. 13-cis retinoic acid, a form of vitamin A is effectively used in the treatment of acne. Vitamin A being a powerful antioxidant helps to clear the pores by flushing toxins and free radicals outside the body.
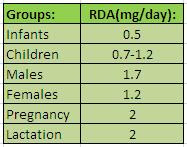
Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamin A:
 The above chart lists the RDA for different age groups. However, the recommended dosage of vitamin A in order to fight acne is 8,000 IU per day but if you are pregnant do not take more than 5000 IU per day.
The above chart lists the RDA for different age groups. However, the recommended dosage of vitamin A in order to fight acne is 8,000 IU per day but if you are pregnant do not take more than 5000 IU per day.Dietary Sources of Vitamin A:


The best plant sources of Vitamin A or carotene are yellow and dark green leafy vegetables and fruits like spinach, amaranth, broccoli, carrots, pumpkin, mango, papaya, apricots, yams etc. The best animal sources of vitamin A or retinol are liver, kidney, egg yolk, milk, butter, cheese, fish liver oils etc.
Deficiency Effects:
Deficiency of vitamin A makes the skin rough and dry. It leads to keratinization of skin tissues which can increase bacterial infection and ultimately leads to the formation of acne.
Overconsumption Effects:
High doses of Vitamin A can also cause pimples. The side effects include skin irritation, itchiness, dryness, redness and puffiness. It is also important to note that overconsumption of vitamin A can be dangerous during pregnancy.
2) B-Complex Vitamins:
Several water soluble B-complex Vitamins like Vitamin B1 (Thiamine), Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin), Vitamin B3 (Niacin), Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) and Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) play an important role in maintaining healthy skin tone. They also contribute in the prevention of stress acne by reducing internal stressors like tension, anxiety, worry and anger since many studies proves stress as an important factor in aggravating and maintaining acne. It is also recommended to eat a variety of fruits and vegetables to obtain all the essential B-Complex Vitamins as these vitamins work together in a group. Some facts about essential B-Complex Vitamins are listed below.
I) Vitamin B1 (Thiamine):


Dermatological Functions:
Vitamin B1 is important for energy production and assists in proper digestion during the process of food metabolism. A proper balance of this vitamin helps the body in the absorption of other vitamins. It is also known to enhance the process of blood circulation. Vitamin B1 being a powerful antioxidant helps to clear the pores by flushing toxins and free radicals outside the body.
Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamin B1:
 The recommended dosage of Thiamine in order to fight acne is 10 mg 3 times per day.
The recommended dosage of Thiamine in order to fight acne is 10 mg 3 times per day.Dietary Sources of Thiamine:
 The best sources of Vitamin B1 or Thiamine are yeast, cereals, pulses, brown rice, flax seeds, oil seeds, nuts, asparagus, cauliflower, potatoes, orange, pork, liver, eggs, milk etc.
The best sources of Vitamin B1 or Thiamine are yeast, cereals, pulses, brown rice, flax seeds, oil seeds, nuts, asparagus, cauliflower, potatoes, orange, pork, liver, eggs, milk etc.Deficiency Effects:
Deficiency of Thiamine can lead to weakness, constipation and edema.
II) Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin):

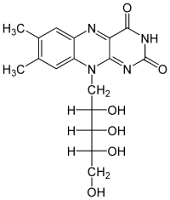
Dermatological Functions:
Vitamin B2 is essential for the maintenance of healthy skin, hair and nails. It works along with B1 to improve and maintain the mucus membranes in the digestive tract and thus assists in proper digestion and energy production.
Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamin B2:
 The recommended dosage of Riboflavin in order to fight acne is 10 mg 3 times per day.
The recommended dosage of Riboflavin in order to fight acne is 10 mg 3 times per day.Dietary Sources of Riboflavin:
The best sources of Riboflavin are milk and milk products, meat, eggs, liver, cereals, fruits, vegetables and fish.
Deficiency Effects:
Deficiency of Riboflavin can cause different types of Acne.
III) Vitamin B3 (Niacin):


Dermatological Functions:
Vitamin B3 is important for a healthy skin as it enhances the process of blood circulation. It helps in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins. It helps to flush the toxins out of the cell.
Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamin B3:
 The recommended dosage of Niacin in order to fight acne is 100 mg 3 times per day.
The recommended dosage of Niacin in order to fight acne is 100 mg 3 times per day.Dietary Sources of Niacin:
The best sources of Niacin are liver, yeast, whole grains, cereals, pulses like beans and peanuts, milk, fish, eggs and vegetables.
Deficiency Effects:
Deficiency of Niacin can also cause different types of Acne.
IV) Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid):

Dermatological Functions:
Vitamin B5 is popular for reducing stress and acne relief. It is also important for the proper functioning of the adrenal glands. It plays a vital role in the production of Coenzyme A which is important for the metabolism of skin oils.
Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamin B5:
 The recommended dosage of Pantothenic acid in order to fight acne is 50 mg 3 times per day.
The recommended dosage of Pantothenic acid in order to fight acne is 50 mg 3 times per day.Dietary Sources of Pantothenic Acid:
The best sources of Pantothenic acid are egg, liver, meat, yeast, milk, fruits and vegetables.
Deficiency Effects:
Deficiency of Pantothenic acid can be a cause of stress acne and hormonal acne.
V) Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine):


Dermatological Functions:
Vitamin B6 is important in the metabolism of proteins, sugars and fatty acids. It is also important in maintaining a healthy immune system and producing antibodies.
Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamin B6:
 The recommended dosage of Pyridoxine in order to fight acne is 50 mg 3 times per day.
The recommended dosage of Pyridoxine in order to fight acne is 50 mg 3 times per day.Dietary Sources of Pyridoxine:
The best sources of Pyridoxine are egg yolk, fish, milk, meat, wheat, corn, cabbage, roots and tubers.
3) Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid):


Dermatological Functions:
Vitamin C is very important for growth and repair of skin tissues and thus directly helps in maintaining healthy skin. Vitamin C being an antioxidant protects against infection and enhances immunity. Along with bioflavonoids Vitamin C can have an antibacterial effect in fighting acne. It speeds up the absorption of certain minerals like iron and thus speeds up in the process of healing acne.
Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamin C:
 The recommended dosage of vitamin c in order to fight acne is 300 mg 3 times per day but if you are suffering from diabetes it is recommended to consult the physician about the proper dosage of vitamin c.
The recommended dosage of vitamin c in order to fight acne is 300 mg 3 times per day but if you are suffering from diabetes it is recommended to consult the physician about the proper dosage of vitamin c.Dietary Sources of Vitamin C:


The best sources of vitamin c are all citrus fruits like orange, gooseberry, guava, plum, Kiwi, lemon and green vegetables like cabbage, spinach, tomatoes and potatoes. Milk is a poor source of Vitamin C or Ascorbic acid.
Deficiency Effects:
Deficiency of vitamin c can increase the chance of a skin infection. It can also slow down the process of healing acne.
4) Vitamin E:
Vitamin E is a fat soluble vitamin that exists in 8 different forms.

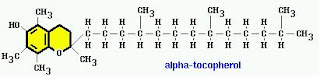
Dermatological Functions:
Vitamin E is a naturally occurring antioxidant that enhances the acne healing process and tissue repair. It also protects the skin from being damaged by excess UV radiation. It prevents the cell damage by preventing the oxidation of polyunsaturated fats. It also protects the body from damage by free radicals.
Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamin E:
 The recommended dosage of vitamin E in order to fight acne is 400 IU per day.
The recommended dosage of vitamin E in order to fight acne is 400 IU per day.Dietary Sources of Vitamin E:
 The best sources of vitamin E are wheat germ oil, cotton seed oil, peanut oil, corn oil, sunflower oil, meat, milk, butter and eggs.
The best sources of vitamin E are wheat germ oil, cotton seed oil, peanut oil, corn oil, sunflower oil, meat, milk, butter and eggs.5) Vitamin K:


Dermatological Functions:
Vitamin K is essential for the production of blood clotting factors and the repair of broken capillaries. It speeds up the healing process. It helps in repairing the skin that has been damaged by dryness or discoloration due to acne. It is very popular for its anti-aging ability to remove fine lines, spider veins and dark circles under the eyes.
Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamin K:
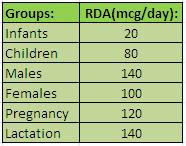
Dietary Sources of Vitamin K:
 The best sources of vitamin k are green leafy vegetables like spinach, cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli, tomatoes and alfa alfa. It is also present in egg yolk, meat, liver, cheese and other dairy products.
The best sources of vitamin k are green leafy vegetables like spinach, cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli, tomatoes and alfa alfa. It is also present in egg yolk, meat, liver, cheese and other dairy products.Deficiency Effects:
The persons with the deficiency of vitamin k would take a longer time to repair the skin that is damaged due to acne. Another visible deficiency effects are spider veins and dark circles under the eyes.
Overconsumption Effects:
High doses of vitamin K produce hemolytic anemia due to increased breakdown of RBC.
6) Zinc:
Dermatological Functions:
Zinc prevents acne by regulating the activity of sebum production by sebaceous glands. Zinc promotes a healthy immune system, helps in wound healing and prevents scarring. It is also an antioxidant which helps to clear the pores by flushing toxins and free radicals outside the body.
Recommended Daily Intake of Zinc:
 The recommended dosage of Zinc in order to fight acne is 20 mg per day.
The recommended dosage of Zinc in order to fight acne is 20 mg per day.Dietary Sources of Zinc:
 The best sources of zinc are oysters, liver, beef, wheat, cheese, shrimp, egg, milk and fruits
The best sources of zinc are oysters, liver, beef, wheat, cheese, shrimp, egg, milk and fruitsDeficiency Effects:
The deficiency of zinc can be one of the causes of formation of varied types of acne.
Overconsumption Effects:
High doses of zinc can cause severe stomach pains as zinc is a heavy metal.
7) Chromium:
Dermatological Functions:
Chromium fights against acne by reducing skin infections.
Recommended Daily Intake of Chromium:
The recommended dosage of chromium in order to fight acne is 150 mcg per day.
Dietary Sources of Chromium:
Chromium is not easily absorbed from food sources and moreover high quantities of sugar in the diet causes a loss of chromium from the body. Thus, in order to get adequate amount of chromium in the diet, it should be taken in the supplemental form called as chromium picolinate or chromium polyicotinate.
8) Selenium:
Selenium aids skin elasticity and helps in acne relief by diminishing skin inflammation. It is an antioxidant that inhibits the oxidation of fats and protects vitamin E. Selenium is required in trace amounts by the body. Generally selenium deficiency is not seen in healthy individuals but high doses of selenium of about 400 mg/day are highly toxic.
Labels:
Acne Vitamins
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
